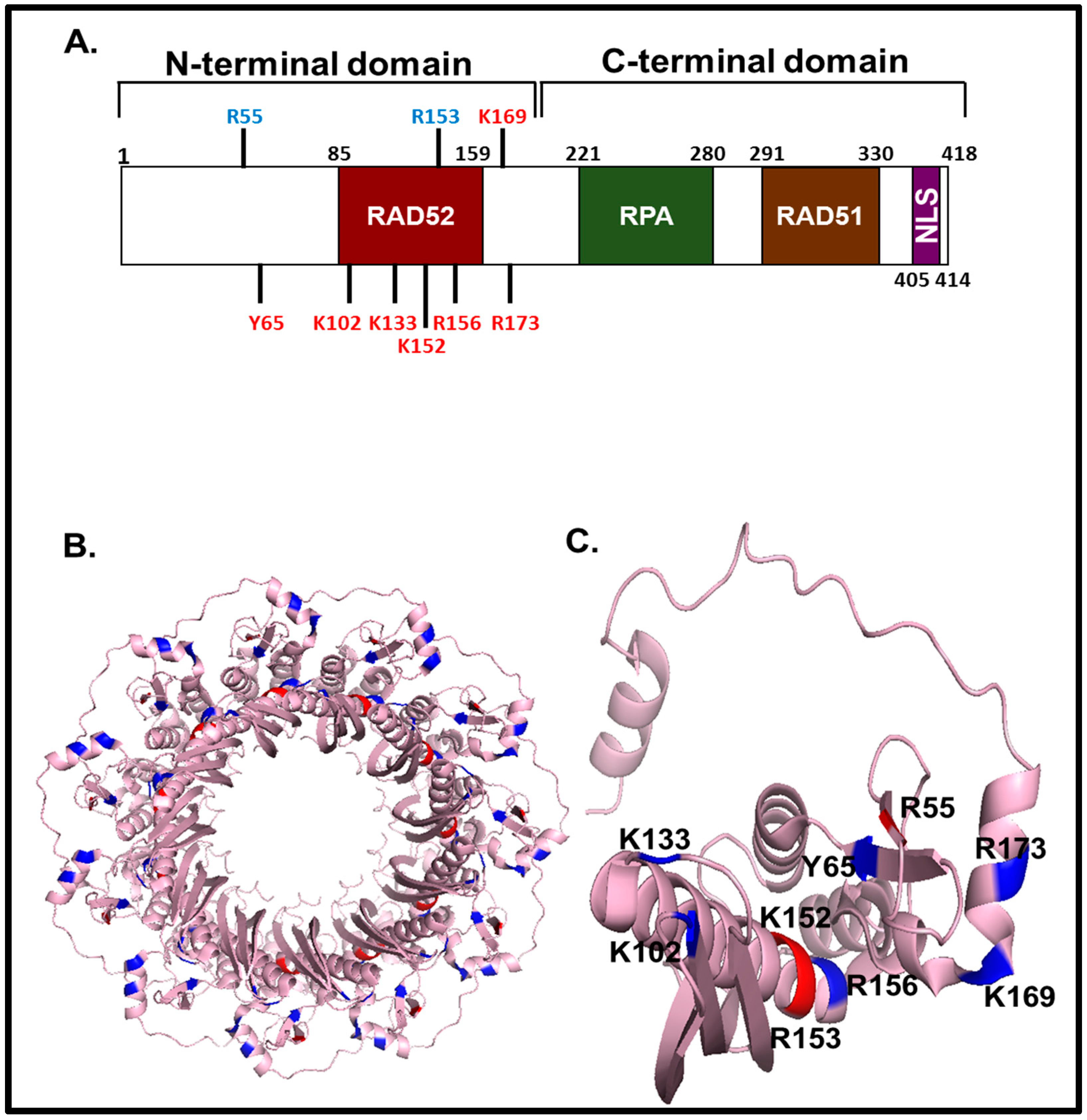
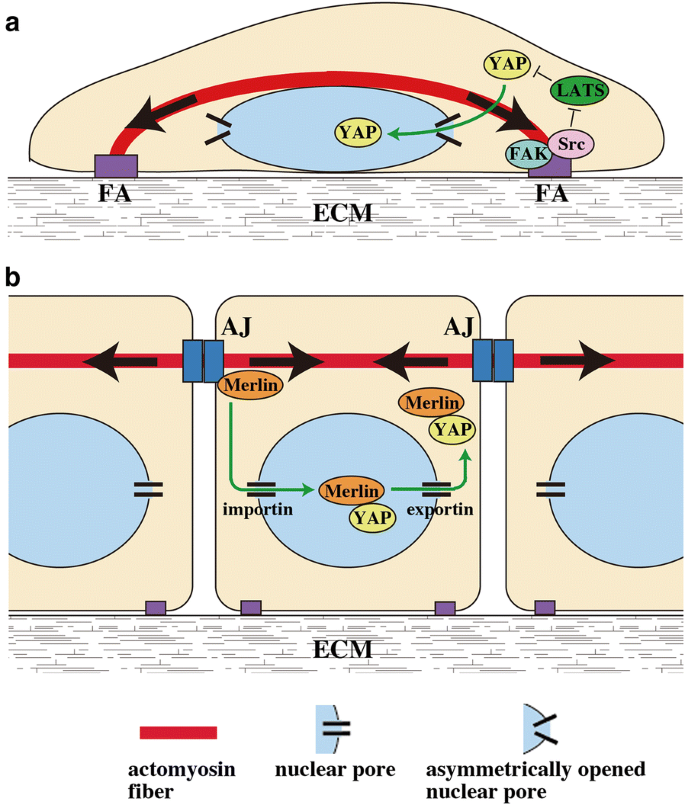
Crystallographic analysis of the specific yet versatile recognition of distinct nuclear localization signals by karyopherin alpha. Autoinhibition by an internal nuclear localization signal revealed by the crystal structure of mammalian importin alpha. Here we report the crystal structure of the nuclear import adaptor importin a1 bound to the nuclear localization signal nls of ebna lp that shows ebna lp residues 44 rrvrrr 49 binding to the major nls binding site at the p0 p5 positions.
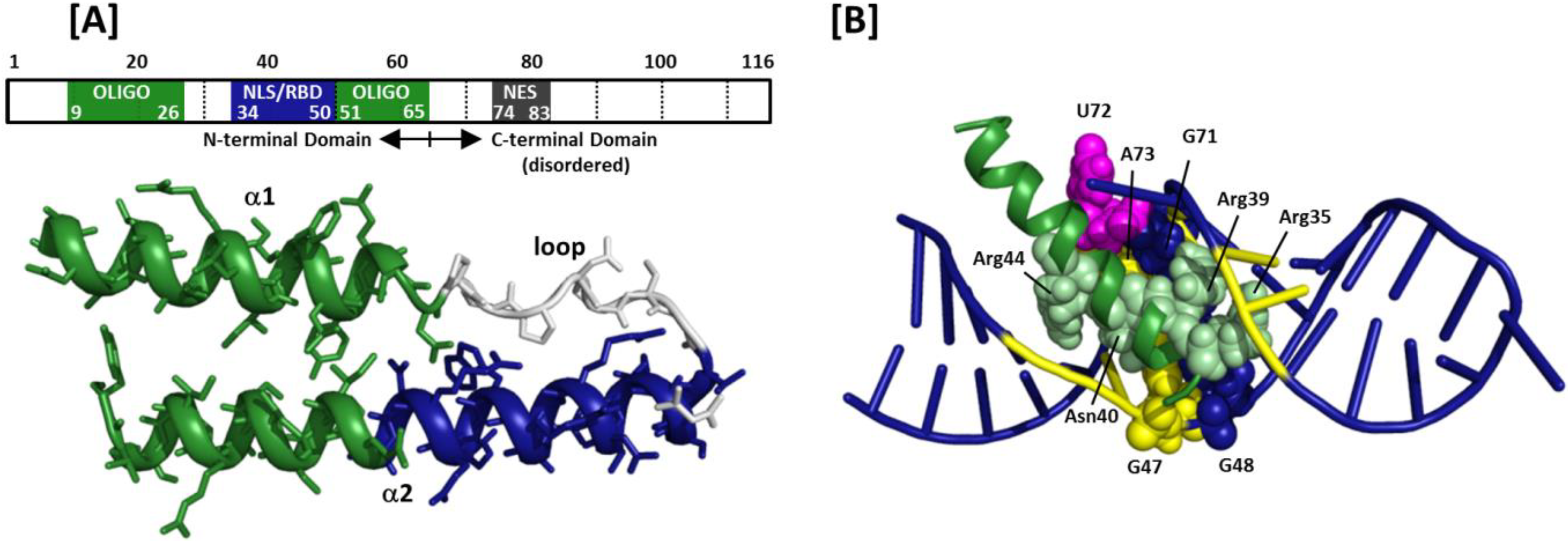
Nuclear localization of ebna lp is essential for cooperation with ebna2. The structure of mouse importin α has been determined at 2 5 å. Importin α is the nuclear import receptor that recognizes classical monopartite and bipartite nuclear localization signals nlss.

2 mg ml of reverse sequence nls bsa was added to 100 μl of hss followed by the addition of 40 μg ml biotinylated nls bsa. Biotin was coupled to the conjugated proteins. Nls peptides and reverse sequence nls peptides were conjugated to bovine serum albumin bsa.
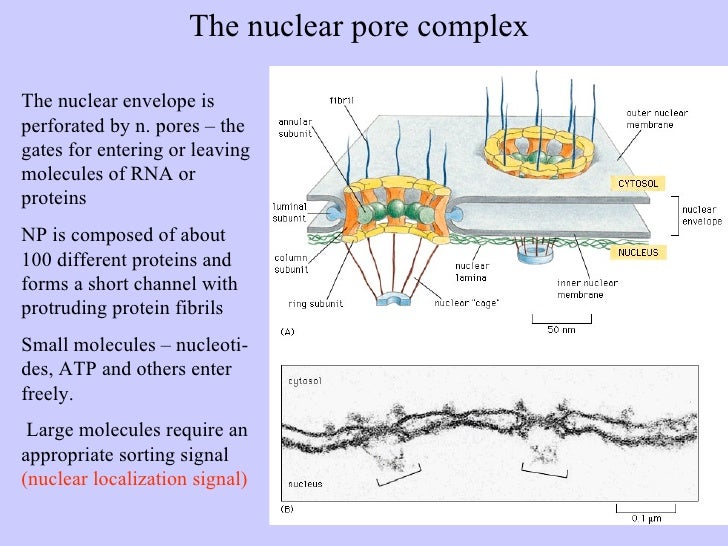
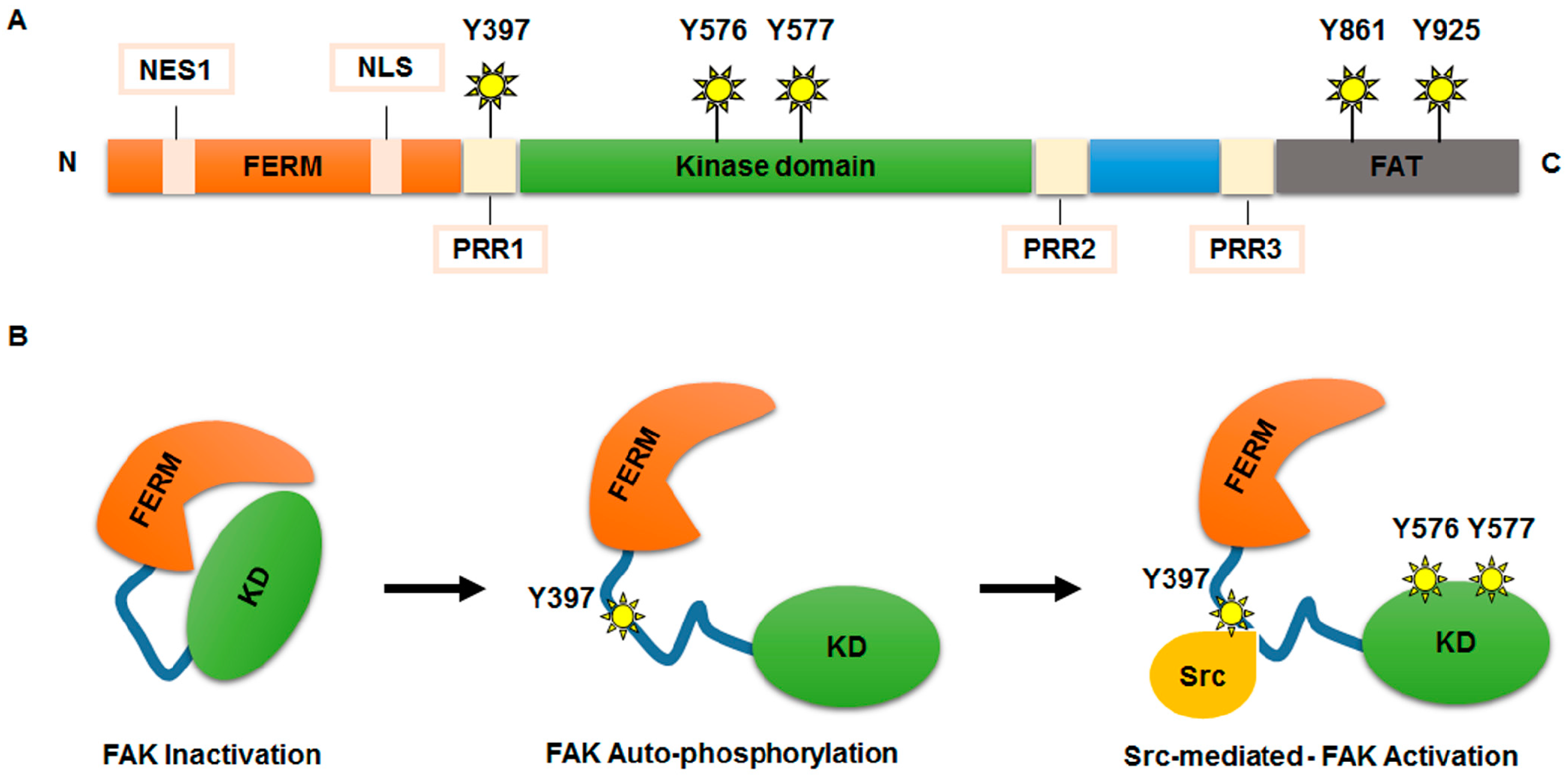
Nuclear localization signal binding assay. In this pathway a protein containing a classical basic nuclear localization signal nls is imported by a heterodimeric import receptor consisting of the β karyopherin importin β which mediates interactions with the nuclear pore complex and the. The best understood system for the transport of macromolecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus is the classical nuclear import pathway.
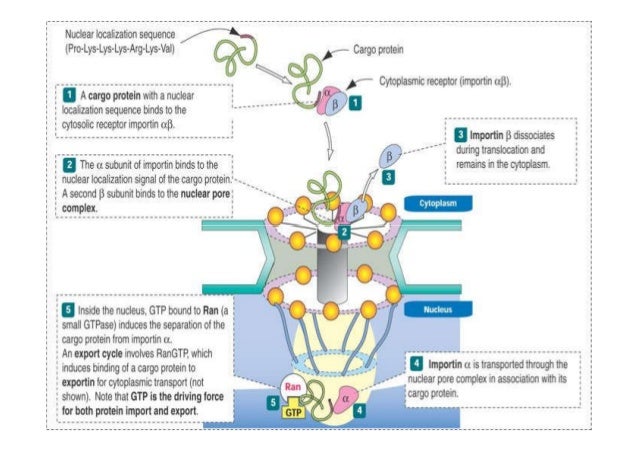
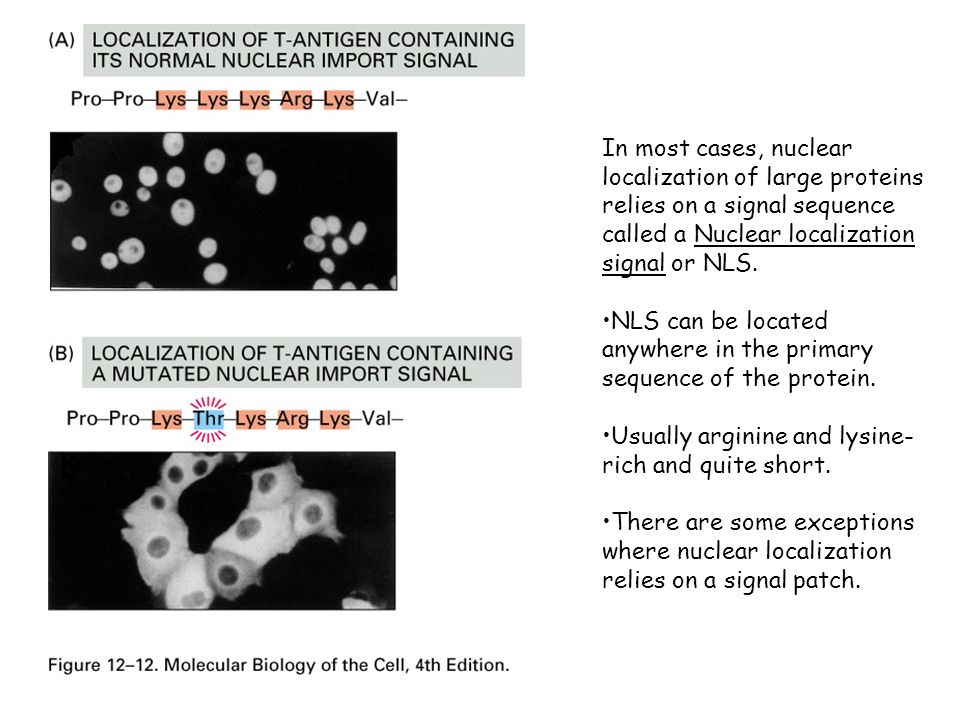
Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same nls. A nuclear localization signal or sequence nls is an amino acid sequence that tags a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport typically this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface.